Introduction to Mazdutide
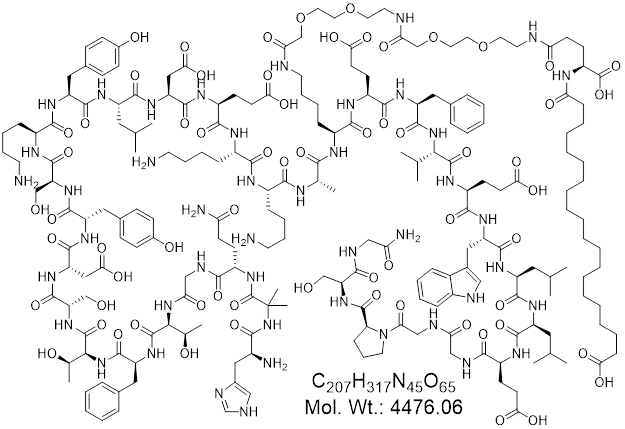
Mazdutide (also known as IBI362 or LY3305677) is an innovative therapeutic peptide designed to address metabolic disorders through a dual-agonist mechanism. It is currently under investigation for managing obesity, type 2 diabetes, and related cardiometabolic conditions, showing promising results in clinical trials.
Mechanism of Action
Mazdutide is a dual agonist of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucagon receptors (GCGR), functioning as an analog of oxyntomodulin (OXM). Activation of GLP-1 receptors enhances insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner, reduces appetite, and delays gastric emptying, improving glycemic control and promoting weight loss. Concurrently, glucagon receptor activation increases energy expenditure and lipid mobilization, further aiding weight reduction and improving liver fat metabolism. This dual mechanism synergistically targets key pathophysiological aspects of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Key Research Areas
Mazdutide is currently being studied in preclinical and clinical research settings for its potential effects on metabolic processes. Research investigations are focused on its ability to modulate pathways related to body weight regulation, glucose metabolism, and lipid handling. Ongoing studies are examining its impact on experimental models of obesity, type 2 diabetes, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), and conditions associated with altered cardiovascular function, such as heart failure with preserved or mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFpEF/HFmrEF). Additionally, its observed effects on serum uric acid levels in laboratory settings have prompted exploratory studies into metabolic regulation of purine metabolism. In current experimental protocols, mazdutide is typically administered via subcutaneous injection, with ongoing research exploring the feasibility of alternative formulations. All research involving mazdutide is conducted in controlled, non-human environments and is intended for investigational purposes only. This compound is not approved for human use.
Certificate of Analysis