Introduction to MOTS-C 10mg
MOTS-C 10mg is a synthetic peptide derived from a mitochondrial-encoded peptide sequence. It is primarily utilized in research settings to investigate its role in regulating metabolic pathways and cellular energy homeostasis.
Mechanism of Action
MOTS-C functions by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of energy metabolism. Through this pathway, MOTS-C influences glucose uptake, insulin sensitivity, and mitochondrial function, making it a molecule of interest in studies related to metabolic health.
Research Applications
MOTS-C 10mg is used in experimental research to explore:
Cellular metabolism and energy regulation
Insulin signaling pathways
Potential interventions for metabolic disorders
Effects on physical performance and endurance in model systems
Usage Notice
This product is intended exclusively for laboratory research. MOTS-C 10mg is not for human or veterinary use or consumption and should be handled according to applicable safety standards.
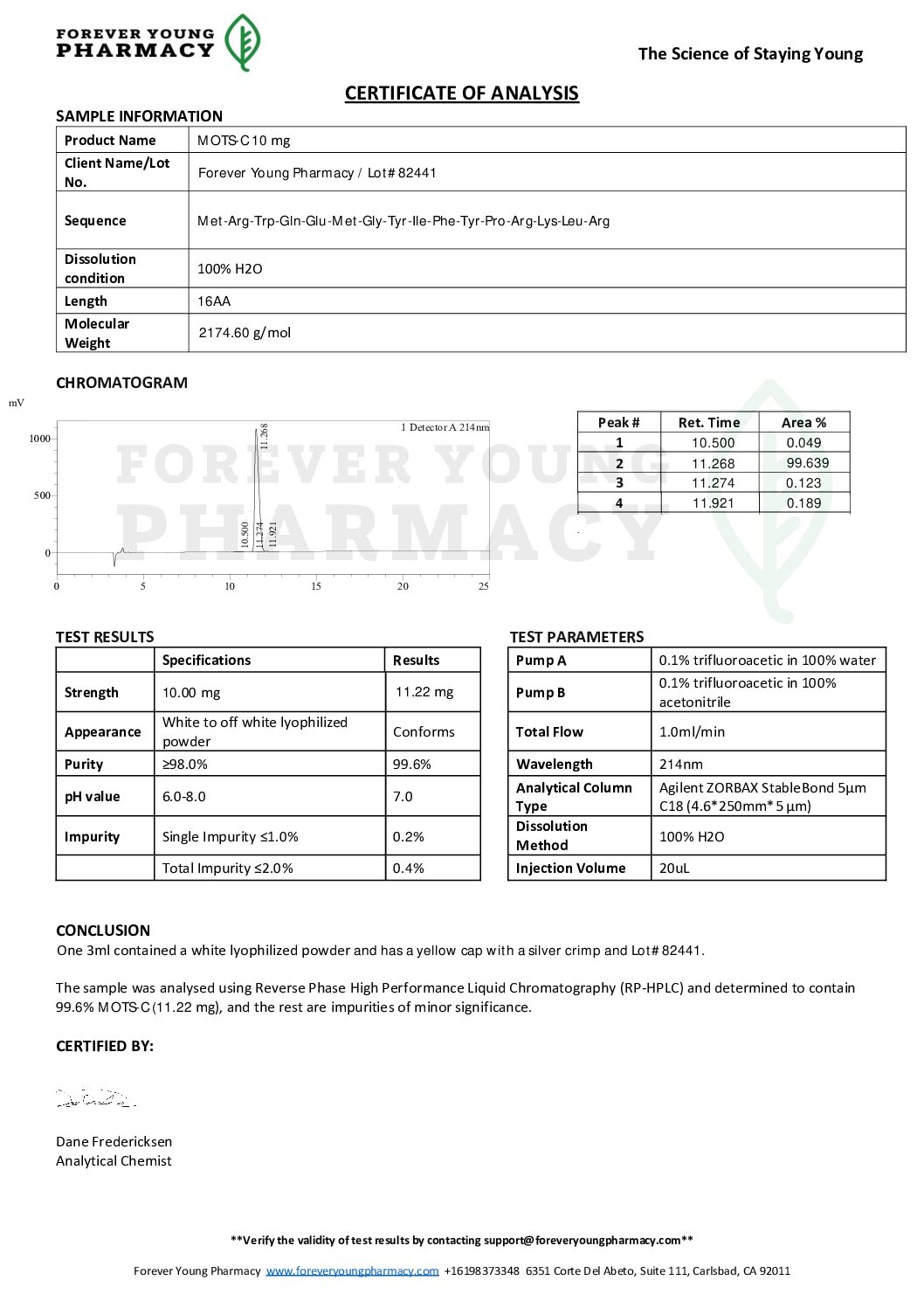
Certificate of Analysis
| Property | Description |
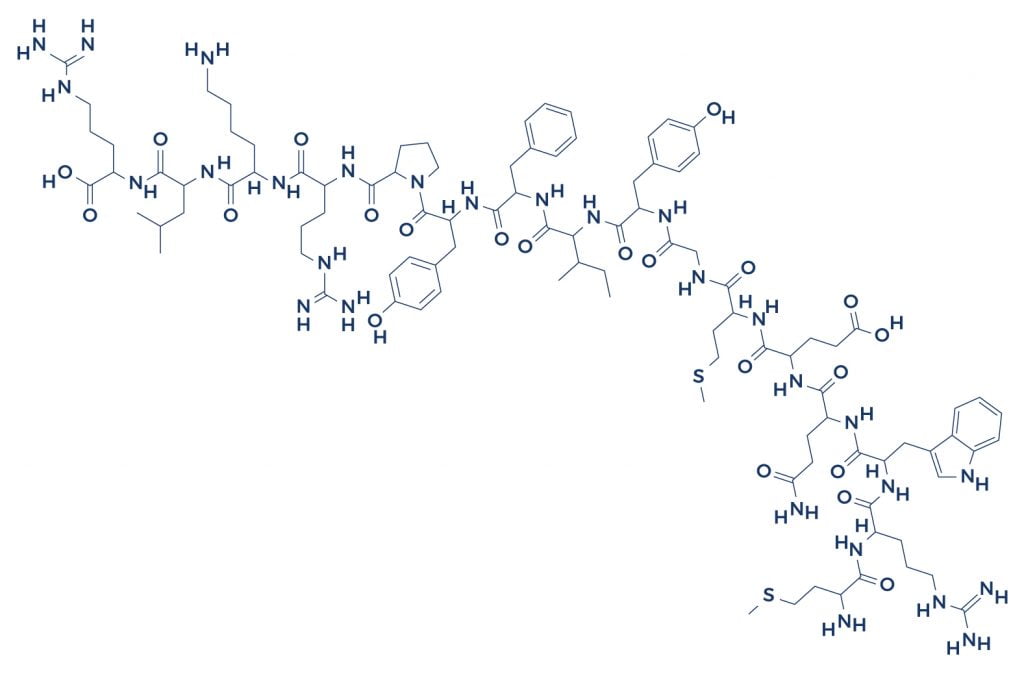
| Chemical Sequence | H-Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Glu-Met-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-OH2 |
| CAS | 1627580-64-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C101H152N28O22S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 2174.62 g/mol |
| CID | N/A |
| Appearance | White Lyophilized Powder |
Learn More About MOTS-C
- “Mots-c Dosage: The Future of Metabolic Enhancement” – This article explores the impact of MOTS-c on aging, cardiovascular disease, insulin-resistance, and inflammation. It also discusses its role in diseases and its effects on bone metabolism
- “Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c, Diabetes, and Aging-Related Diseases” – This review focuses on recent advances in MOTS-c research with regards to diabetes, including both type 1 and type 2. It provides insight into the development of new therapies for diabetes and other age or senescence-related diseases
- “MOTS-C Peptide Dosing: A New Frontier in Metabolic Health” – This article delves into the development and application of MOTS-C, its role in regulating bone metabolism, and the potential pathways through which exercise can promote bone health