Introduction to Melanotan II
Melanotan II is a synthetic peptide developed for research purposes to study its effects on melanin production and pigmentation. It is a modified analog of the alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) and interacts with melanocortin receptors, primarily the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), to stimulate melanin synthesis in pigment-producing cells.
Mechanism of Action
Melanotan II binds to MC1R receptors on melanocytes, triggering intracellular signaling pathways that increase melanin production. This process results in skin darkening or tanning, which is of interest in research related to pigmentation and protection against ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Key Research Areas
Investigating mechanisms of melanin synthesis and regulation
Studying potential protective effects against UV-induced cellular damage
Exploring implications for pigmentation disorders such as vitiligo
Examining effects on appetite and neurobehavioral responses
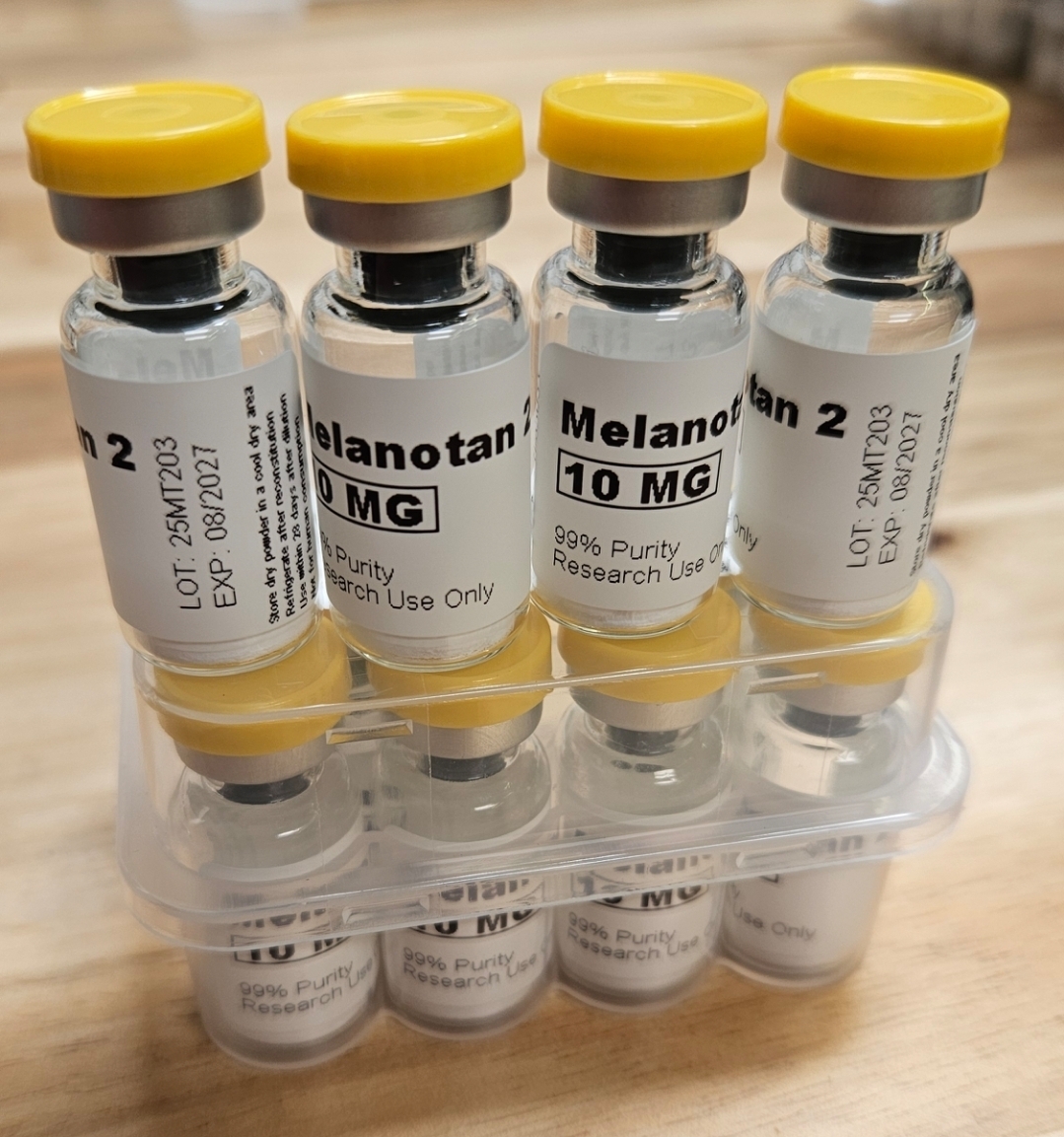
Cerificate of Analysis
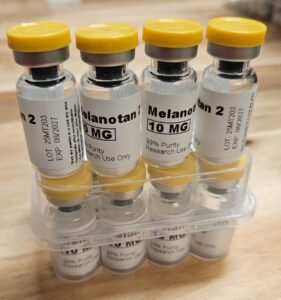
Actual Product You Will Receive
| Property | Description |
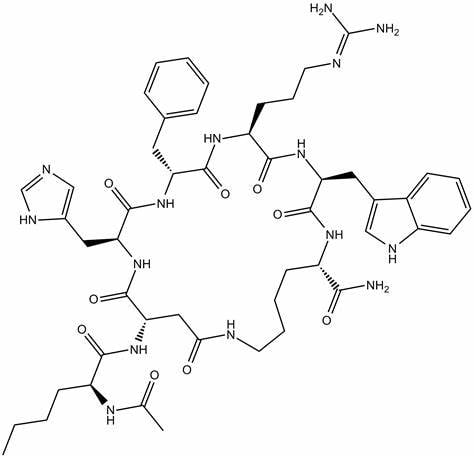
| Chemical Sequence | Ac-Nle-cyclo [Asp-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Lys]-NH2 |
| CAS | 121062-08-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C50H69N15O9 |
| Molecular Weight | 1024.18 g/mol |
| CID | 92432 |
| Appearance | White Lyophilized Powder |
Important Notice
Melanotan II is strictly intended for laboratory and scientific research only. It is not approved for human consumption, medical use, or cosmetic application. Its safety and efficacy for use in humans have not been established, and it should be handled in accordance with all applicable research protocols and regulations.